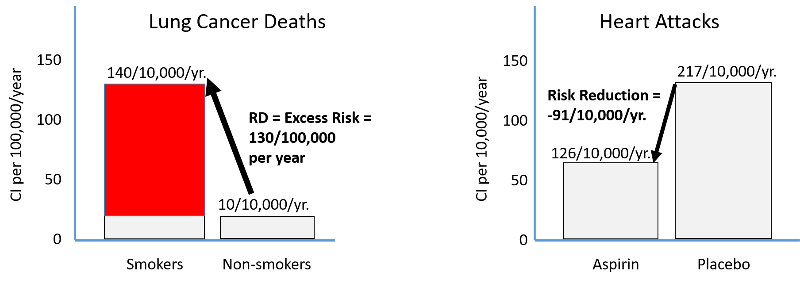
1 Increased risk of outcome – RR = 1 No risk of outcome – RR <1 Reduced risk of outcome 4First off, this five times represents what is called relative risk Relative Risk Relative risk is a ratio of the risks of two groups In the example described above, it would be the risk of heart attack for a person in their current condition compared to the risk of heart attack if that person were in the normal ranges However, to truly interpret the severity of a relative risk we have to

Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February
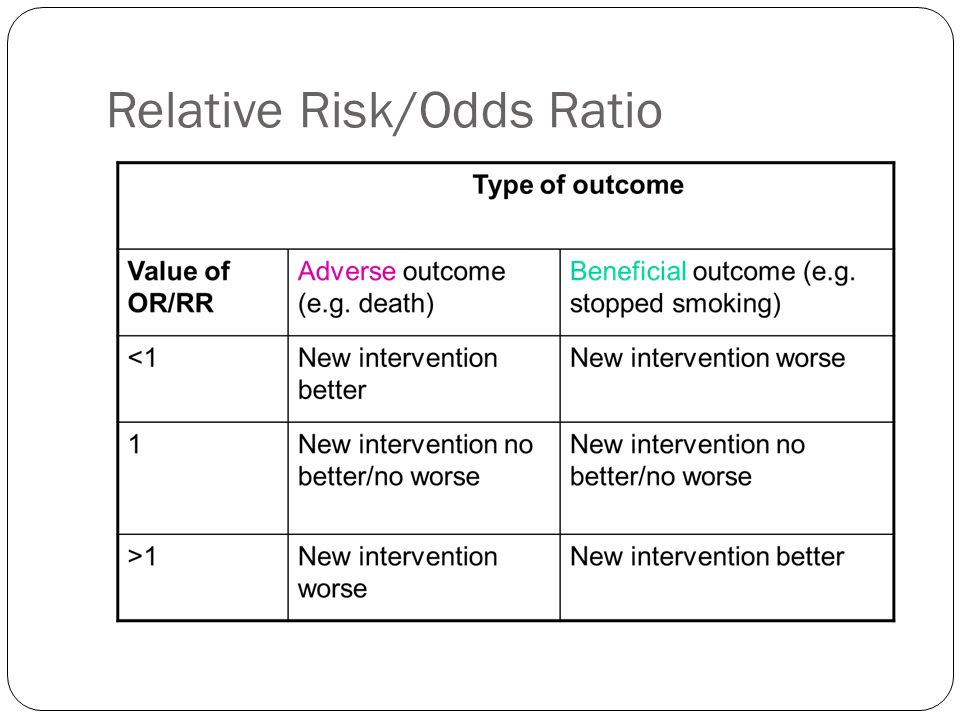
Why is odds ratio better than relative risk
Why is odds ratio better than relative risk-The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the placebo group However, this wouldThe adjusted odds ratio suggests little or no association between E and D, contradicting the crude analysis This suggests a serious potential for confounding (2) BD2REC There are 10 singleyear agestrata (ages 0 through 9) The question is whether odds ratios are heterogeneous (H 0 OR 1 = OR 2 = = OR 10 vs H 1 at least on age



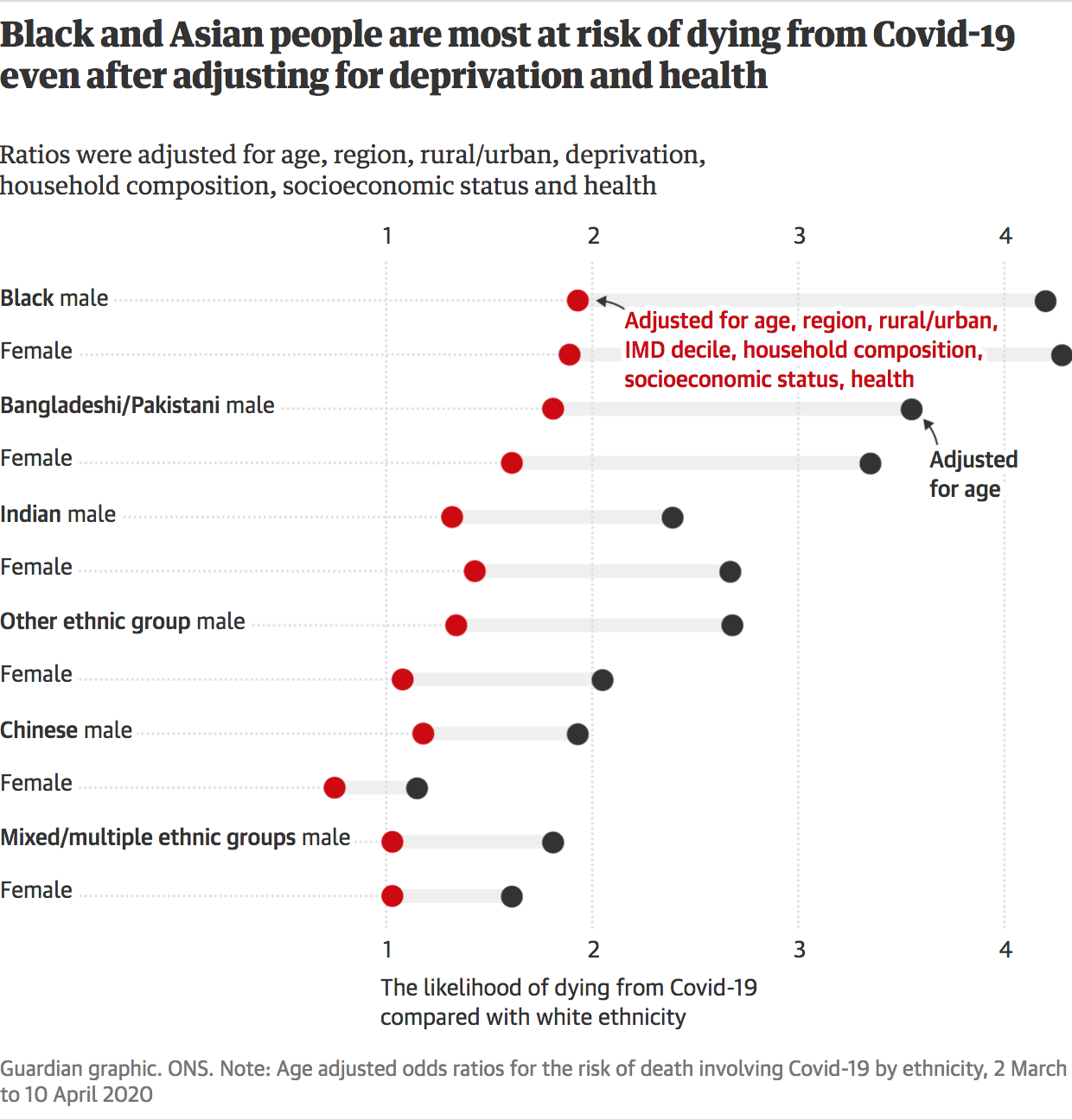
Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia
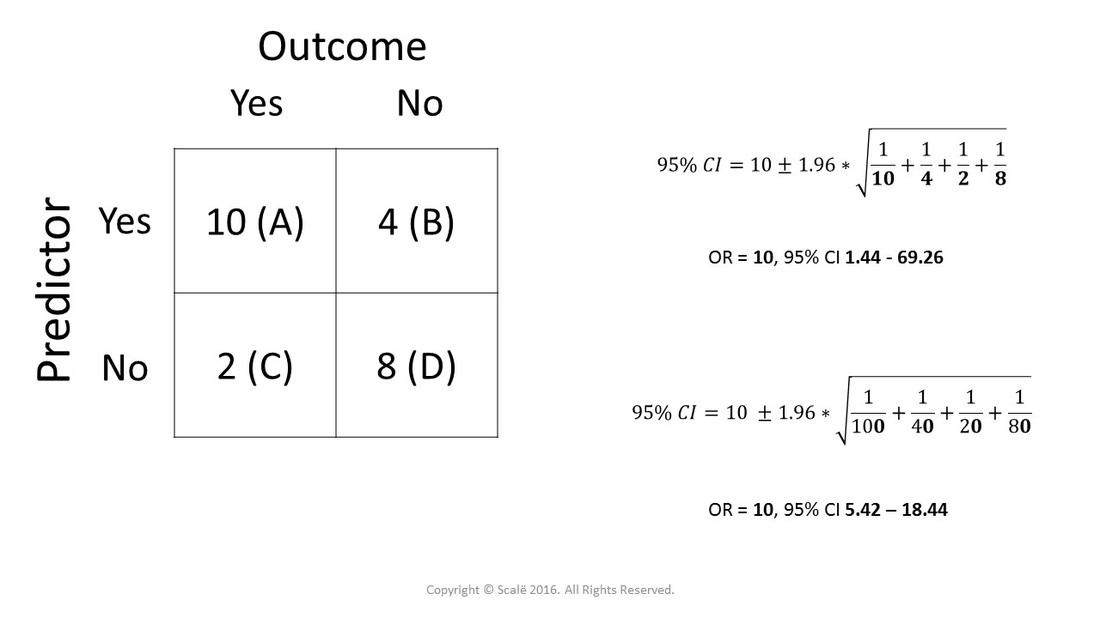
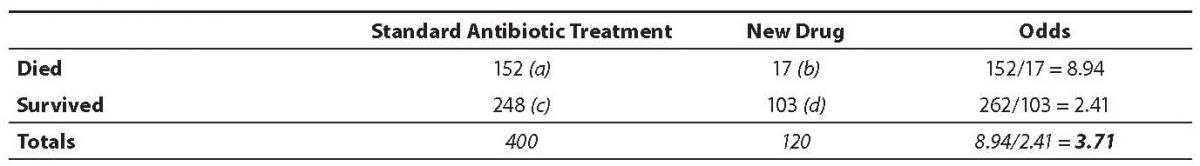
Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;The odds ratio supports clinical decisions by providing information on the odds of a particular outcome relative to the odds of another outcome In the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocol Relative risk assessment statistics are particularly suitedSometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR >
Relative risk vs odds ratio Relative risk and odds ratio are often confused or misinterpreted Especially while coefficients in logistic regression are directly interpreted as (adjusted) odds ratio, they are unwittingly translated as (adjusted) relative risks in many public health studies In that relative risks are useful in many thousands of applications, along with odds ratio, we proposeAn odds ratio of 05 would mean that the exposed group has half, or 50%, of the odds of developing disease as the unexposed group In other words, the exposure is protective against disease Is odds ratio a measure of risk?0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR <
Odds ratios, relative risk, and β0 from the logit model are presented Keywords st0041, cc, cci, cs, csi, logistic, logit, relative risk, case–control study, odds ratio, cohort study 1 Background Popular methods used to analyze binary response data include the probit model, discriminant analysis, and logistic regression Probit regression is based on the probability integral3 Relative Risk (Risk Ratio) • Expresses how many times more (or less) likely an exposed person develops an outcome relative to an unexposed person • Interpretation – RR >The odds ratio and the relative risk will not always disagree by this much Large effects on groups with high initial risk seem to cause the most problems See Davies et al (1998) for some useful guidelines for when the odds ratio and relative risk are likely to differ When they do differ, the relative risk represents the typical interpretation that most people make There are some




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Solved Please Answer All Questions Parts Step By Step Chegg Com
Cases 1 and 4 have the same absolute risk reduction, NNT, and odds ratios, but very different relative risk, relative risk reduction, and risk at baseline Real Example The following example 18 is a prospective study, which compares the incidences of dyskinesia after ropinirole (ROP) or levodopa (LD) in patients with early Parkinson's diseaseThe basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program At the start of the school year they impose the newOdds ratio vs risk ratio in randomized controlled trials Postgrad Med 15 May;127(4) doi / Use of odds ratio (OR) in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) has been criticized because it overestimates the effect size, if incorrectly interpreted as risk ratio (RR) To what extent does this make a difference in the context of clinical research is
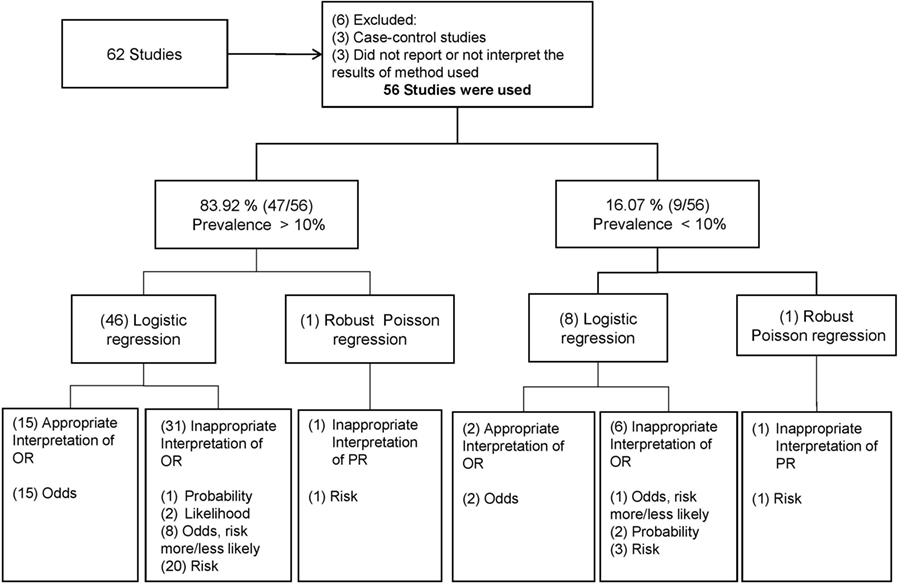



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science
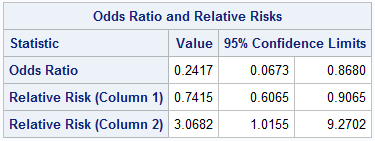



Statistics Basics Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Calculation In Excel Bi Practice
Odds ratio vs risk ratio You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers divided by the total number of smokers) and among nonsmokers (the same, but with nonThe Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard) Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed to the treatment Odds is the numberMethods The purpose of this paper is to illustrate, using examples, how each measure is used, what it means, and what are its advantages




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
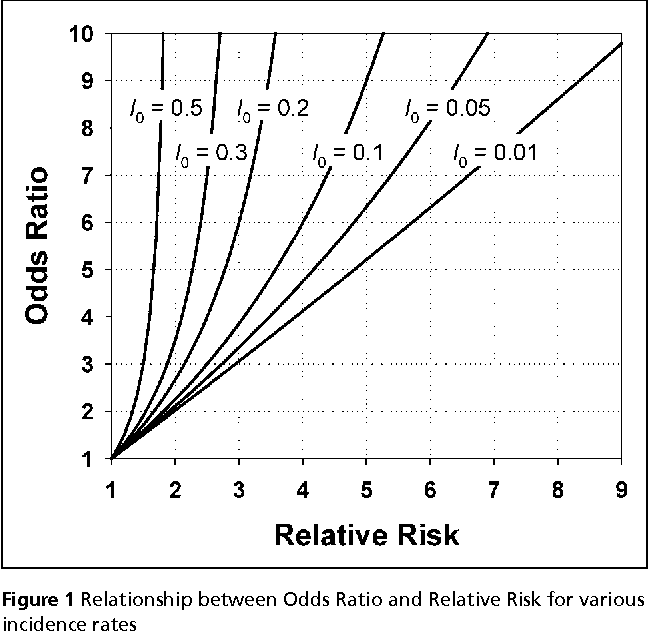
The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, Odds ratios, like odds, are more difficult to interpret (Sinclair 1994, Sackett 1996) Odds ratios describe the multiplication of the odds of the outcome that occur with use of the intervention To understand what an odds ratio means in terms of changes in numbers of events it is simplest to firstSafety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsRelative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk What S The Difference Statology
The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,Examples of measures of association include risk ratio (relative risk), rate ratio, odds ratio, and proportionate mortality ratio Risk ratio Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group It does so by dividing the risk (incidenceAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy &
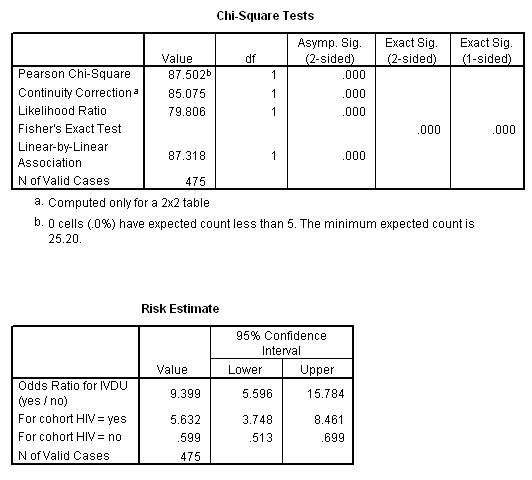



Marg Innovera




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
In every other way the hazard ratio is similar to odds ratio and relative risk wherein treatment efficacy is denoted by a hazard ratio of less than 10 in prevention trials and a hazard ratio of more than 10 in treatment trials Table 3 Hazard ratio and timetoevent analysis 1 In a randomised controlled trial, 441 patients assessed on admission as having low to moderate riskOdds Ratio (OR) and Relative Risk (RR) are two ratios often used in the epidemiology studies and the clinical trials They are related, but the calculation and the interpretation are quite different Notice that the Relative Risk (RR) may also be called Risk Ratio with the same abbreviation of RR Relative Risk P0=The probability of events (eg, responder, cardiovascularOdds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinction becomes important in cases of




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



1
Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated However, it should be noted that, although, mathematicalA risk ratio is a good measure to use for a metaanalysis if you have data from longitudinal cohorts or clinical trials It is generally thought to be easier to interpret than an odds ratioWhen a study outcome is rare in all strata used for an analysis, the odds ratio estimate of causal effects will approximate the risk ratio;




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy
The odds ratio is a common measure of risk but its interpretation may be hazardousOR >1 indicates increasedThe ratio of the risk of healing in the elastic bandage group to the risk in the inelastic bandage group is called the risk ratio For Table 4, the risk ratio = 0538/0284 = 1 The risk ratio is also called the relative risk and the rate ratio, all of which can be conveniently abbreviated to RR



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy
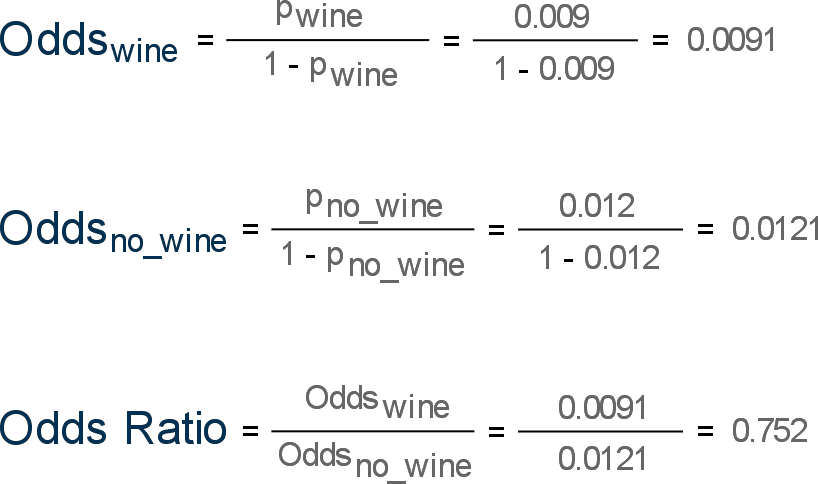
In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 If the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative risk vs Odds ratioThe relative risk is different from the odds ratio, although the odds ratio asymptotically approaches the relative risk for small probabilities of outcomesIf IE is substantially smaller than IN, then IE/(IE IN) IE/IN Similarly, if CE is much smaller than CN, then CE/(CN CE) CE/CN Thus, under the rare disease assumption = () () = In practice the odds ratio is commonly used forThis is why the first study yielded odds ratios and not relative risk Once they got the results and found smoking to have the strongest association, they reversed the roles and did a cohort study looking at smokers and nonsmokers (now the independent variable) and compared their lung cancer status (now the dependent variable), yielding relative risk ratios The difference is the




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia
Unless I'm mistaken, the equation explained above does not properly describe Odds Ratio, it describes Relative Risk Odds Ratio is the odds that the diseased group was exposed, divided by odds that the nondiseased group was exposed (a/c)/(b/d) in the classic table Relative Risk is the risk of developing disease in the exposed/interventionMenu location Analysis_Clinical Epidemiology_Risk In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies In prospective studies, Attributable risk or risk difference is used to quantify risk in the exposed group that is attributable to the exposure In retrospectiveThe following example shows how to calculate and interpret an odds ratio and relative risk in a reallife situation Example Calculating Odds Ratio an d Relative Risk Suppose 100 basketball players use a new training program and 100 players use an old training program At the end of the program we test each player to see if they pass a certain skills test The following




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Relative And Absolute Risk Osmosis
How to Interpret Risk Ratios Since the relative risk is a simple ratio, errors tend to occur when the terms more or less are used Because it is a ratio and expresses how many times more probable the outcome is in the exposed group, the simplest solution is to incorporate the words times the risk or times as high as in your interpretation If you are interpreting aExample #1 Interpreting Odds Ratios Researchers want to know if a new treatment improves the odds of a patient experiencing a positive health outcome compared to an existing treatment The following table shows the number of patients who experienced a positive or negative health outcome, based on treatment The odds of a patient experiencing a positive outcome0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4




A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine



Silo Tips
Mainly to distinguish it from relative risk, which is the risk for one group compared to the risk for some other group Basic statistic workshop organised by The Global Health Network Nigerian Regional Faculty 13 The risk ratio In practice, risks and odds for a single group are not nearly as interesting as a comparison of risks and odds between two groups For risk you can make theseTherefore, odds ratios from most casecontrol studies can be interpreted as risk ratios However, if a study outcome is common, the odds ratio will be further f The relative merits of risk ratios and odds ratios Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 09Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table




Risk Risk Difference Relative Risk Youtube




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science
Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not probability Again, the OR willOdds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why thatRisk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while a 12 paper




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence
RR and OR are commonly used measures of association in observational studies In this video I will discuss how to interpret them and how to apply them to patRELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO The relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other groupCommon measures are odds ratios, relative risk, relative risk reduction, absolute risk reduction, and the number needed to treat The question faced by the practitioner is then Which one will help me in choosing the best treatment for my patient?



1




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February
Percent, population attributable risk percent, relative risk, odds, odds ratio, and others The concept and method of calculation are explained for each of these in simple terms and with the help of examples The interpretation of each is presented in plain English rather than in technical language Clinically useful notes are provided,In a recent article, Davies et al (1) commented on a potential problem when interpreting odds ratios (OR) as relative risks (RR) in epidemiological studies However, their vague concept of effect measures as applied to different study designs in epidemiology may lead to misuse and false interpretation of OR Davies et al (1) state that the odds ratio is a commonOdds Ratio (OR) is a measure of association between exposure and an outcome The OR represents the odds that an outcome will occur given a particular exposure, compared to the odds of the outcome occurring in the absence of that exposure Important points about Odds ratio Calculated in casecontrol studies as the incidence of outcome is not known;




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




16 Odds Ratios From Casecontrol Studies Casecontrol Studies




Odds Ratio Article




Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People




Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk What S The Difference Statology




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id




Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




The Relationship Between Nnt Calculated From An Odds Ratio Or And An Download Scientific Diagram



Risk Difference Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Quantifying Health




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



1




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




A Most Odd Ratio Interpreting And Describing Odds Ratios Abstract Europe Pmc



Wrnmmc Libguides Com




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



1




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




Estimating Risk




Pin On Las Metricas Del Riesgo




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



Risk Ratio And Risk Difference



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be




Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Interpreting Basic Statistics Ppt Video Online Download




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Sciencedirect




Solved Iv Estimate And Interpret The Relative Risk Chegg Com



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Glossary Of Research Terminology



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



Use And Interpret Chi Square In Spss




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Understanding Relative Risk Odds Ratio And Related Terms As Simple As It Can Get Psychiatrist Com



How To Interpret The Odd Ratio And P Value



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be




Epidemiology Odds Ratio Or Bean Around The World




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj



Hkzto9hkc3ymim




Odds Ratios The Odd One Out Stats By Slough




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Interpretation Of Odds Ratio And Fisher S Exact Test By Sergen Cansiz Towards Data Science




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
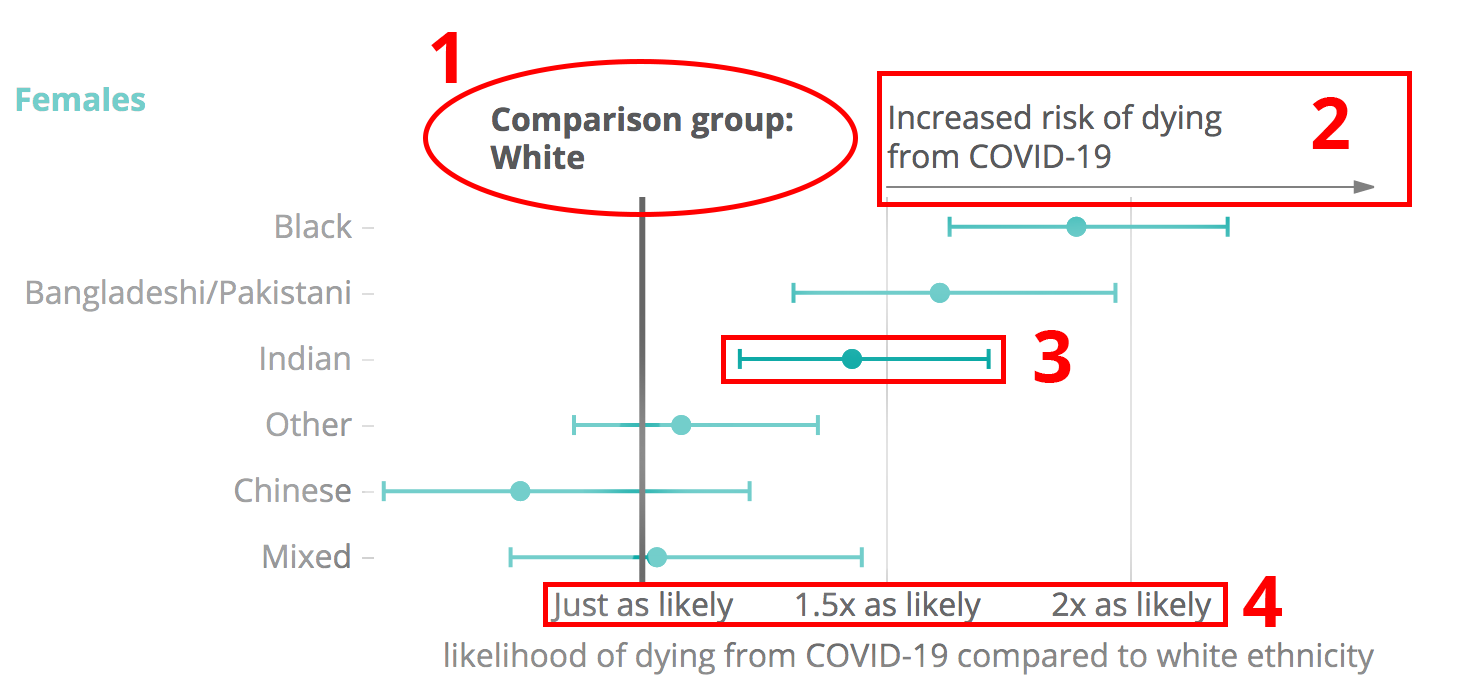



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
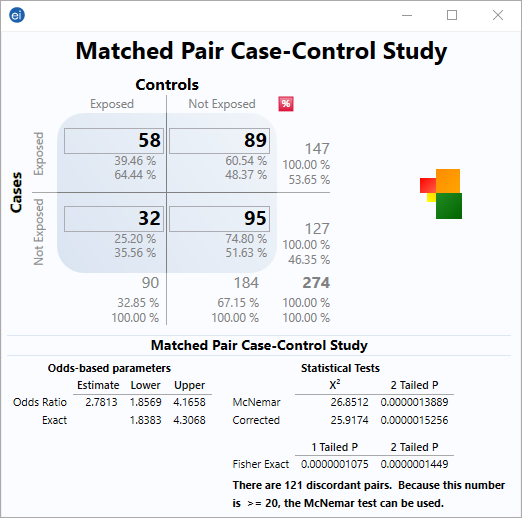



Matched Pair Case Control Statcalc User Guide Support Epi Info Cdc
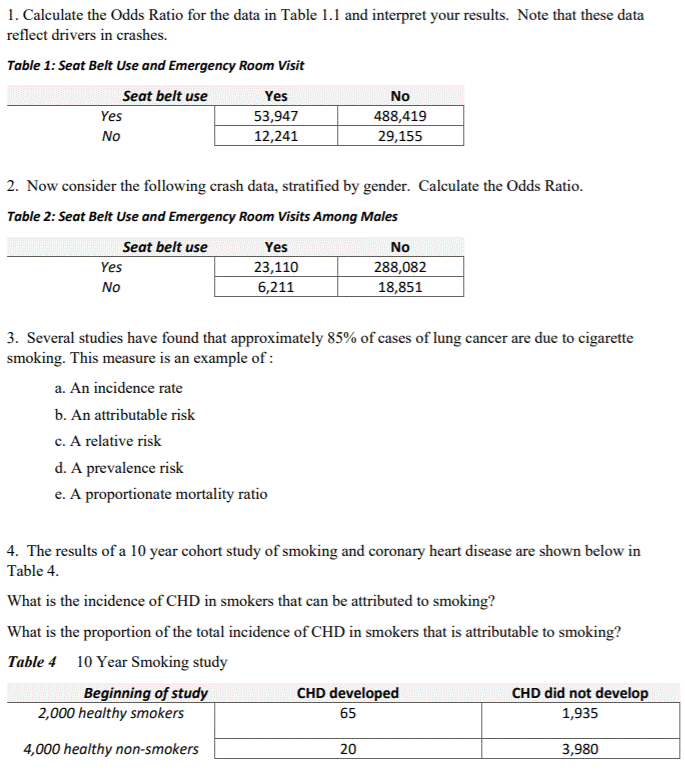



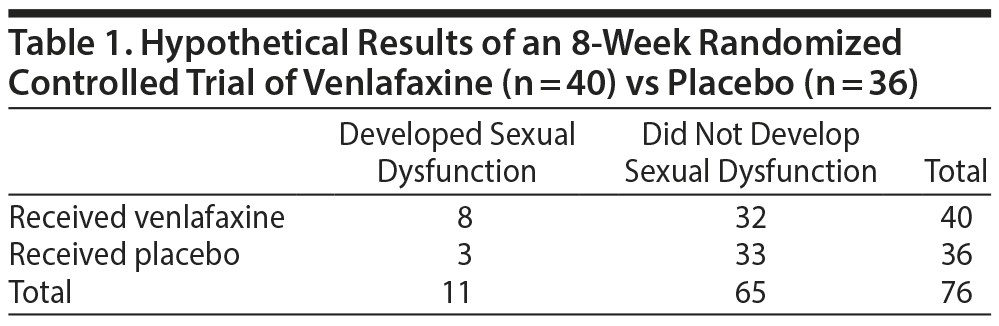
Solved 1 Calculate The Odds Ratio For The Data In Table 1 1 Chegg Com




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Teachepi Org




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow
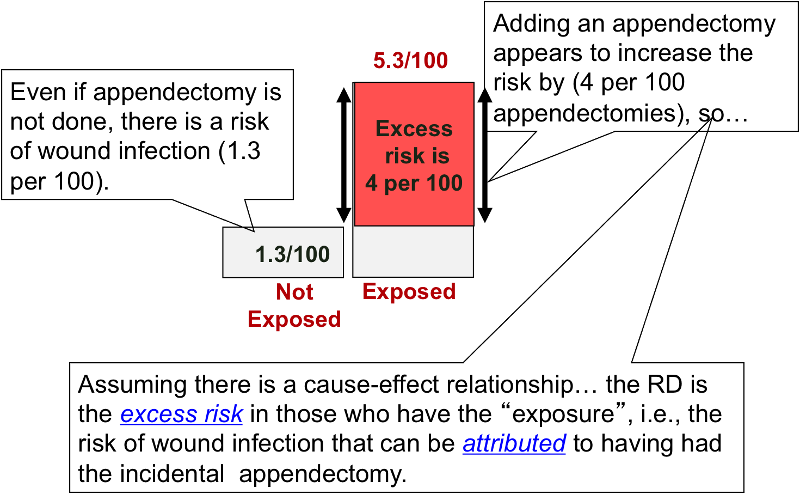



Risk Differences And Rate Differences



Analysis Of Categorical Data




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



The Odds Ratio Calculation Usage And Interpretation Biochemia Medica




Rr Interpretation Http Www Slideshare Net Terryshaneyfelt7 What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean Statistics Math Research Methods Nursing Research



Interpretation Of Genetic Association Studies Markers With Replicated Highly Significant Odds Ratios May Be Poor Classifiers



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿